ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
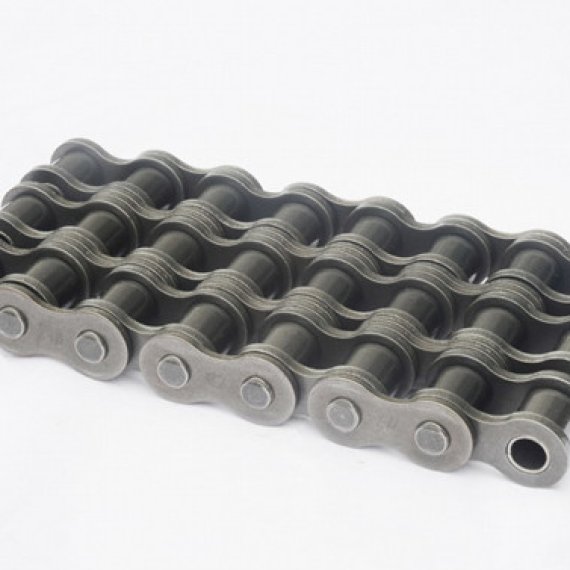
There are two types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having two inner plates held together by two sleeves or bushings upon which rotate two rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of two outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The "bushingless" roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing one step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an abrasive paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a "dry" PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
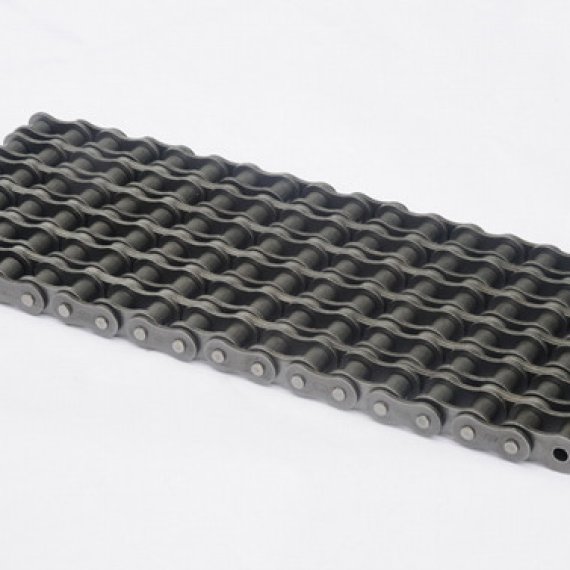
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then one of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be "siamesed"; instead of just two rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be three ("duplex"), four ("triplex"), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has one pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) "riveted" or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of two 'ghost' sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain onto the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle - the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal forward flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
OUR ADVANTAGES
We are professional manufacturer of roller chains, we offer expert advice for design and using of the roller chains for your specific application. High quality and attractive price. We furnish custom-made roller chains with customer's LOGO.